We talked not
too long ago about backup withholding.
What is it?
Think Forms
1099 and you are mostly there.
The IRS
wants reporting for many types of payments, such as:
· Interest
· Dividends
· Rents
· Royalties
· Commissions and fees
· Gambling winnings
· Gig income
Reporting requires
an identification number, and the common identification number for an
individual is a social security number.
The IRS
wants to know that whoever is being paid will report the income. The payor starts
the virtuous cycle by reporting the payment to the IRS. It also means that – if
the payee does not provide the payor with an identification number - the payor
is required to withhold and remit taxes on behalf of the payee.
You want to
know how this happens … a lot?
Pay someone
in cash.
There is a
reason you are paying someone in cash, and that reason is that you probably
have no intention of reporting the payment – as a W-2, as a 1099, as anything –
to anyone.
It is all
fun and games until the IRS shows up. Then it can be crippling.
I had the following bright shiny drop into my office recently:
The client
filed the 1099 and also responded to the first IRS notice.
It could
have gone better.
That 24% is
backup withholding, and I am the tax Merlin that is supposed to “take care of”
this. Yay me.
This case was
not too bad, as it involved a single payee.
How did it
happen?
The client issued
a 1099 to someone without including a social security number. They filled-in “do
not know” or “unknown” in the box for the social security number.
Sigh.
Sometimes you
do not know what you do not know.
Here is a
question, and I am being candid: would I send in a 1099 to the IRS if I did not
have the payee’s social security number?
Oh, I understand
the ropes. I am supposed to send a 1099 if I pay someone more than $600 for the
performance of services and yada yada yada. If I don’t, I can be subject to a
failure to file penalty (likely $310). There is also a failure to provide penalty
(likely $310 again). I suppose the IRS could still go after me for the backup
withholding, but that is not a given.
Let me see: looks
like alternative one is a $620 given and alternative two is a $38,245 given.
I am not
saying, I am just saying.
Back to our
bright shiny.
What to do?
I mentioned
that the payment went to one person.
What if we
obtained an affidavit from that person attesting that they reported the payment
on their tax return? Would that get the IRS to back down?
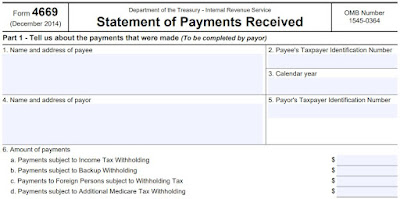
It happens enough that the IRS has a specific form for it.
We filled in
the above form and are having the client send it to the payee. We are
fortunate, as they have a continuing and friendly relationship. She will sign, date,
and return the form. We will then attach a transmittal (Form 4670) and send the
combo to the IRS. The combo is considered a penalty abatement request, and I am
expecting abatement.
Is it a
panacea?
Nope, and it
may not work in many common situations, such as:
(1) One never obtained payee contact information.
(2) A one-off transaction. One did not do
business with the payee either before or since.
(3) The payee moved, and one does not
know how to contact him/her.
(4) There are multiple payees. This could
range from a nightmare to an impossibility.
(5) The payee does not want to help, for whatever
reason.
Is there a
takeaway from this harrowing tale?
Think of
this area of tax as safe:sorry. Obtain identification numbers (think Form W-9)
before cutting someone their first check. ID numbers are not required for
corporations (such as the utility company or Verizon), but one is almost
certainly required for personal services (such as gig work). I suppose it could
get testy if the payee feels strongly about seemingly never-ending tax reporting,
but what are you supposed to do?
Better to
vent that frustration up front rather than receive a backup withholding notice
for $38,245.
And wear out
your CPA.